
FORTE Compact Intra-cloud Discharge Detection Parameterized by
Peak Current
M J Heavner,
D. M. Suszcynsky, A. R. Jacobson, B. D. Heavner, and
D A Smith
LAUR-02-5759
GPS Lightning Sensor
A VHF receiver on a GPS satellite has been used to collect
lightning signatures. For this study, only the event times have
been compared to LASA event times to geolocate the events and
study the physical characteristics as indicated by the LASA
waveform.
Los Alamos Sferic Array
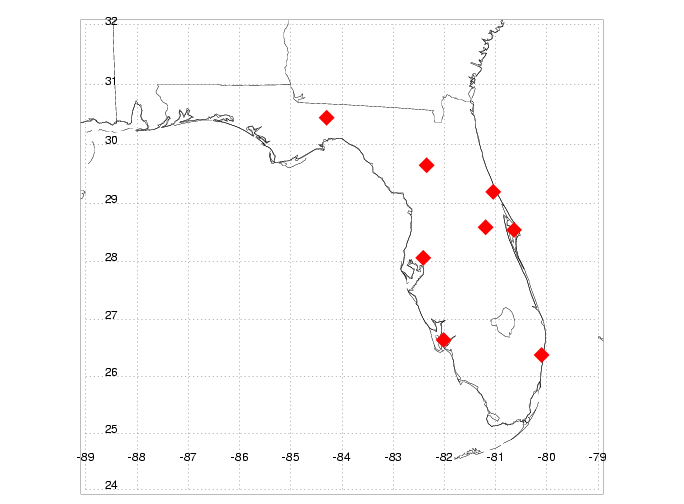
The Los Alamos Sferic Array (LASA) has been described in detail
by [5]. LASA is a collection of
field change meters that has been operated since May 1998 and
has consisted of as many as eight electric field change meters
located in Florida (additional stations have been in NM, CO, NE,
and Brazil). The array stations record and time tag (with
better than 2 us absolute accuracy) triggered field change
waveforms, 24 hours per day. Differential time of arrival
methods are used to geolocate the sources, and then lightning
events are classified and characterized. Over seven million
lightning discharges have been processed by the array over more
than four years of operation.
FORTE
The FORTE satellite, launched Aug. 1997, has instrumentation
capable of making both radio frequency and optical observations
of lightning. The orbit altitude is approximately 820 km at an
inclination of 70., providing at most ~15 minutes
coverage of any ground spot. The FORTE RF payload consists of
two tunable 22 MHz receivers and one tunable 85 MHz bandwidth
receiver. The FORTE radio systems and typical observations are
described by [3]. The FORTE optical
package consists of a fast, non-imaging photometer and a slower
CCD array. The FORTE satellite has collected over 4 million VHF
waveforms since its launch in August 1997.
Links to:






